The circular economy is a relatively new economic model that enables sustainable economic development, where waste products are continuously recycled and reinvested in new production. This significantly reduces waste, limits its negative impact on the environment and increases resource efficiency.
Traditional linear economics aims to achieve profit through low costs of raw materials and the production process, to create economic wealth and success for a large number of companies. Goods acquired by consumers are discarded once they are no longer needed, spoil or become obsolete. Practice shows that we keep less than 5% of the products we buy.

Linear economics depends on two basic premises:
1. The permanent availability of non-renewable resources that can be put into production
2. The provision of sufficient waste disposal sites
The inadequacies of the linear economy lead to a steady worsening of environmental problems due to the growing amounts of waste and their negative impacts on air, water and biodiversity. The ever-increasing demand for energy, the increase in agricultural and all other production needed to meet the needs of a growing population are contributing to a further disturbance of the ecological balance. Therefore, growth based on extracting more and more resources and then disposing of them is limited. It has a threshold beyond which it cannot continue to exist, develop and profit.
Therefore, a new economic model based on the circular economy. It is based on a strategy to conserve natural resources so that all people on Earth can achieve an acceptable level of prosperity without destroying their planet on the way to achieving it.
In a circular economy, the value of products and materials is preserved for as long as possible. Resources are used as efficiently as possible, waste is minimised, and when a product reaches the end of its life cycle, it is reused to create additional value. The circular economy promotes growth, sustainability and competitiveness in the long term.
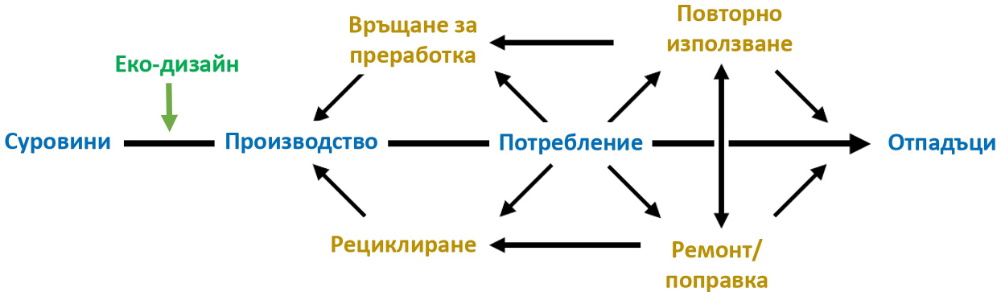
The circular economy is a way to overcome the irreversible damage caused by the depletion of natural resources. It represents a model stimulating the creation of new business opportunities, the introduction of innovative production and consumption methods, and with it specific skills and new jobs.

